Welcome to the first article in our series exploring the components that make up your windows and doors. Whether you’re renovating, building a new home, or simply curious, these articles will guide you through the essentials so you can make informed decisions.

What Is an Insulated Glass Unit (IGU)?
An Insulated Glass Unit (IGU) is a sealed assembly of two or more glass panes separated by a spacer, designed to improve energy efficiency, maintain indoor comfort, and reduce noise. By understanding the inner workings of an IGU, you’ll appreciate why it’s often considered the heart of a modern window.
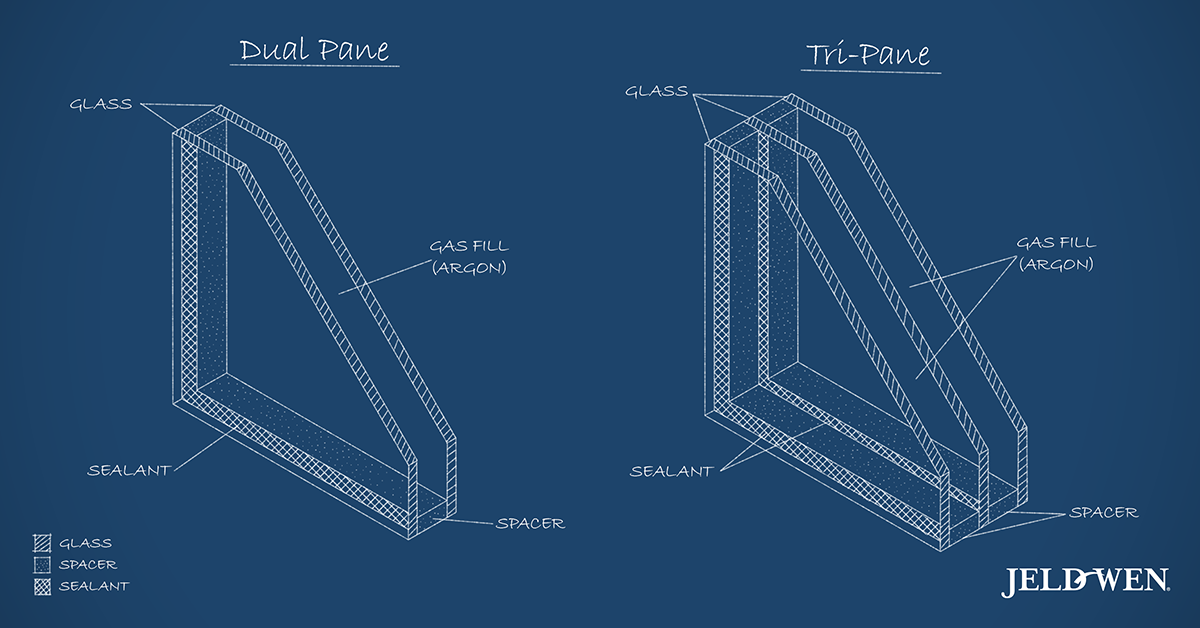
Key Components of an IGU:
- Glass Panes: IGUs typically feature two or three layers of glass. More panes mean better insulation and performance, especially in challenging climates.
- Spacer: The spacer maintains a consistent gap between the panes, often filled with an insulating gas like argon or krypton. Spacers also help manage moisture and reduce heat transfer.
- Gas Fill: Denser than air, gases such as argon or krypton improve thermal performance, slowing heat flow and enhancing overall energy efficiency.
- Sealants: High-quality sealants keep the entire assembly airtight, ensuring the gas remains inside and moisture stays out.
- Low-E Coatings: Ultra-thin metallic coatings on the glass surface reflect heat and block harmful UV rays. This helps maintain a steady indoor temperature and protect interiors from sun damage.
Benefits of IGUs:
Energy Efficiency: With better insulation, IGUs keep your home warmer in winter and cooler in summer, which can lower energy bills.
Comfort: By reducing drafts and maintaining consistent temperatures, IGUs create a more comfortable indoor environment.
Noise Reduction: Multiple layers of glass and an insulating gas fill help dampen outside noise, making your home quieter and more peaceful.
Choosing the Right IGU for Your Home
Climate Considerations
Colder Climates
Triple-Pane IGUs: Three panes help retain heat more effectively, reducing energy loss and improving comfort.
Argon Gas Fill: Argon is commonly used to boost insulation.
Low-E Coatings: Specialized coatings reflect heat indoors and reduce energy loss, maintaining warmth.
For example, the JWC8500 series from JELD-WEN of Canada offers triple-pane configurations, advanced Low-E coatings, and argon gas fills to meet stringent energy performance targets in colder regions.
Sunnier Climates
Low-E Coatings: These coatings help reflect solar heat away, reducing cooling costs.
Double-Pane IGUs: In milder conditions, double-pane units often provide sufficient insulation at a more affordable price point.
Energy Goals
High-Efficiency Performance: If reducing energy consumption is a priority, look for triple-pane IGUs, argon fills, and advanced Low-E coatings. Meeting Canada’s 2030 energy efficiency targets, for instance, the JWC8500 series achieves a U-Factor of 0.14 (U.S./I-P) / 0.82 (Metric/SI) and an Energy Rating (ER) of 44.
Comfort and Noise Reduction: For enhanced comfort and quieter interiors, consider thicker glass, triple panes, and quality sealants.
 Specific Needs
Specific Needs
Noise Reduction: Thicker glass and additional panes help mitigate outside sounds.
Safety and Security: Laminated or tempered glass can provide extra protection.
Aesthetics: Tinted or decorative glass can personalize your home’s style while maintaining performance.
By assessing your climate, energy goals, and personal preferences and considering products like the JWC8500 series that combine efficient design with adaptability. You can choose an IGU that meets your needs and elevates your home’s comfort and performance.
Stay tuned for our next article, where we’ll look more closely at glass options and their impact on window performance.
Explore Related Posts














